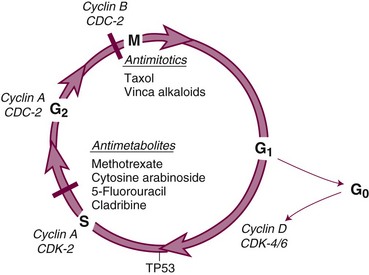
Untitled Document wwwrnceuscom Biology Diagrams The process of cell division, whether normal or cancerous cells, is through the cell cycle. The cell cycle goes from the resting phase, through active growing phases, and then to mitosis (division). The ability of chemotherapy to kill cancer cells depends on its ability to halt cell division.

Keywords: cell cycle arrest, DNA damage, chemotherapy. Introduction. The normal cell cycle consists of complex pathways that regulate the duplication of all molecules and organelles and their separation into two identical daughter cells. This progresses through four phases: G1 (gap), S (synthesis), G2 (gap) and M (mitosis) and is coordinated by How does chemotherapy affect the cell cycle? Different types of chemotherapy drugs attack cancer cells at various stages of the cell cycle. Some target a specific stage of the cycle. Antimetabolites and antifols, for example, target the S stage and interfere with the construction of the DNA molecule. Bleomycin, etoposide, and other agents

How Chemotherapy Drugs Work Biology Diagrams
Cell cycle checkpoints operate as DNA surveillance mechanisms that prevent the accumulation and propagation of genetic errors during cell division. through either radiotherapy or chemotherapy, Chemotherapy works with the cell cycle. Every time any new cell is formed, it goes through a usual process to become a fully functioning (or mature) cell. The process involves a series of phases and is called the cell cycle. Chemotherapy drugs target cells at different phases of the cell cycle. Understanding how these drugs work helps doctors
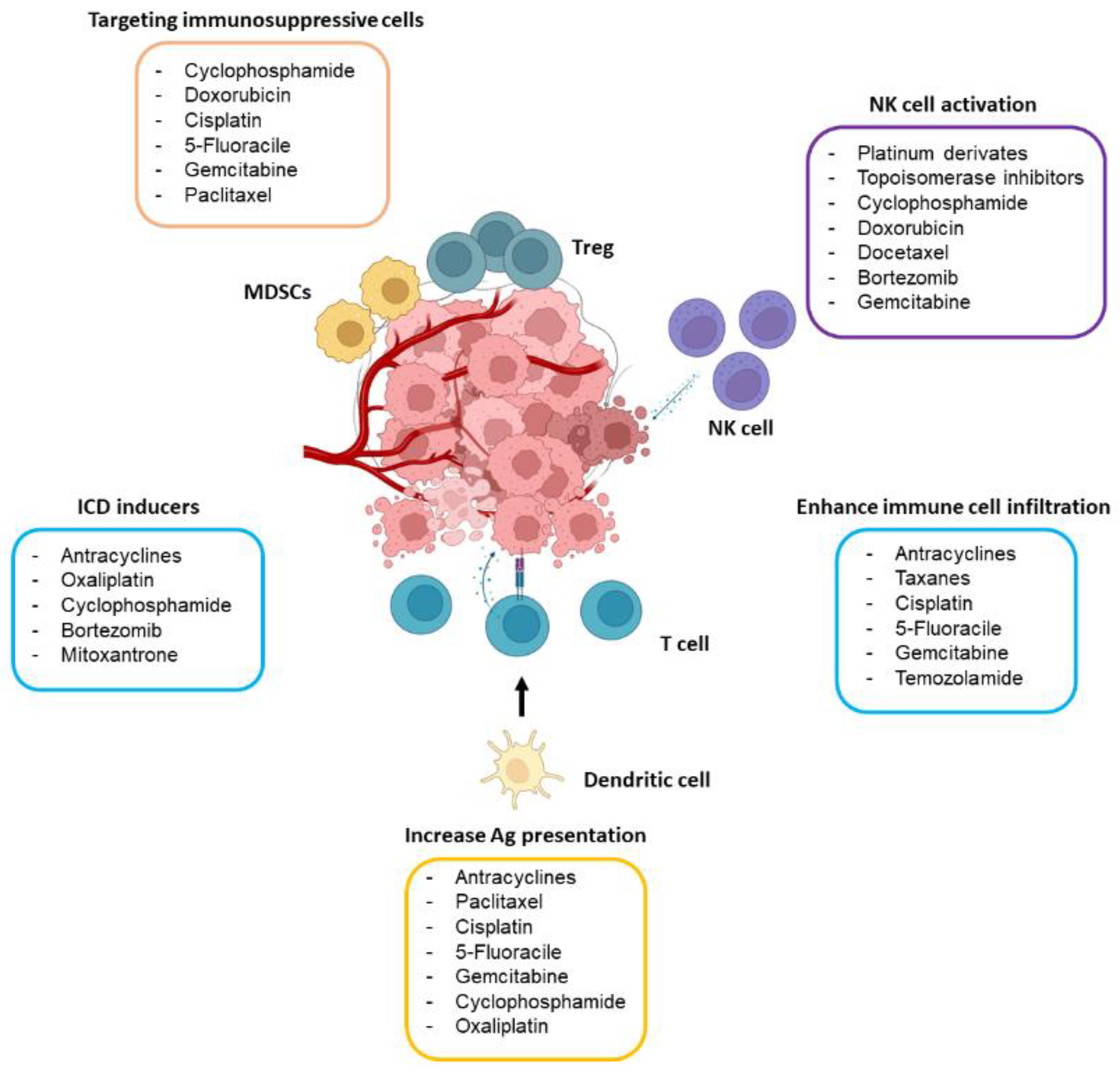
Keywords: chemotherapy, cell cycle regulation, drug delivery systems, combination chemotherapy, cancer therapy. 1. Introduction. Chemotherapy is currently one of the main methods of tumor treatment . However, there are still several obstacles to achieve the desired therapeutic effect. Some inevitable side effects such as nausea and hair loss Chemotherapy class Examples Primary mechanism of action Additional mechanism of action; Antimicrotubule agents: Taxanes (paclitaxel, doxorubicin) Binding to interior surface of microtubules, impeding movement and function ()Altering of cell signaling and trafficking, slowing of cell cycle progression, inhibiting cell migration and invasiveness, disrupting tumor vasculature () The cell cycle is a series of steps, or phases, each cell takes to become a cell, whether it is a healthy cell or a cancerous cell. Chemo works by halting cancer cell division, often by interfering with RNA or DNA synthesis, and shrinking the tumor. The cell cycle goes from a resting phase, to an active phase, then to cell division (called