Food Chain Food Web Examples Definition Activities Biology Diagrams Learn about a food chain in ecology. Get the definition and examples of food chains and see the different types. A food chain is a linear diagram showing how energy moves through an ecosystem. It shows only one pathway out of the many possibilities in a specific ecosystem.

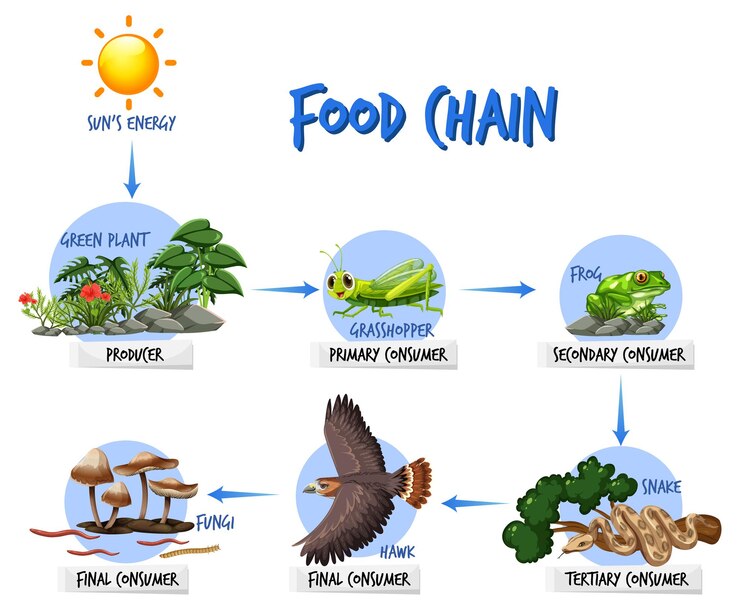
A food chain is a simple way to show the flow of energy in an ecosystem. Each step in the food chain represents an organism that gets its energy by consuming the previous one. A producer traps the solar energy and then provides the basic food or energy for all the other life forms in the ecosystem The consumers or animals derive their energy needs directly or indirectly from the producers Answered Constructing and interpreting simple food chains helps us understand the flow of energy and nutrients within ecosystems. Below are examples of simple food chains, along with explanations of their components and significance. This list of 20 food chain examples, complete with meanings and usage, is an invaluable tool for teachers. Each example portrays a different ecological setting, demonstrating the variety in food chains from simple to complex environments.
20+ Food Chain Examples Biology Diagrams
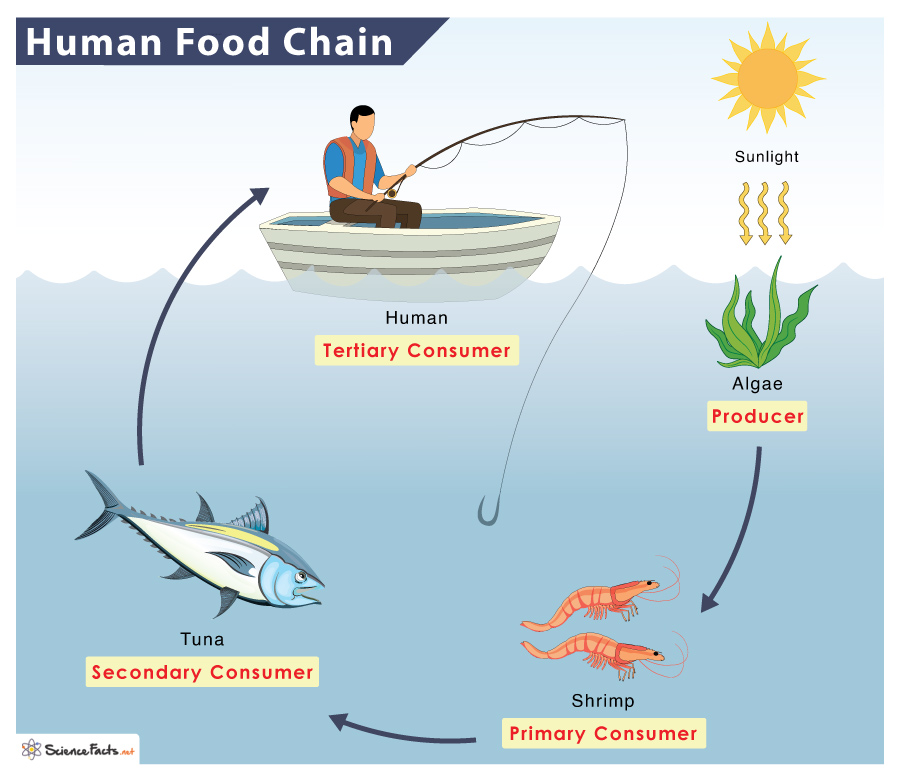
What is a food chain and why does it matter? As these food chain examples show, all living things use it to survive. See types in different ecosystems. Here is an example of a simple food chain: grass → cow → human The grass is the producer. The cow and human are consumers. If one part of a food chain is reduced or changes, the whole food chain is affected. For example if there was a shortage of fish for penguins to eat, penguins would survive less well reducing the food supply for animals further up the food chain.
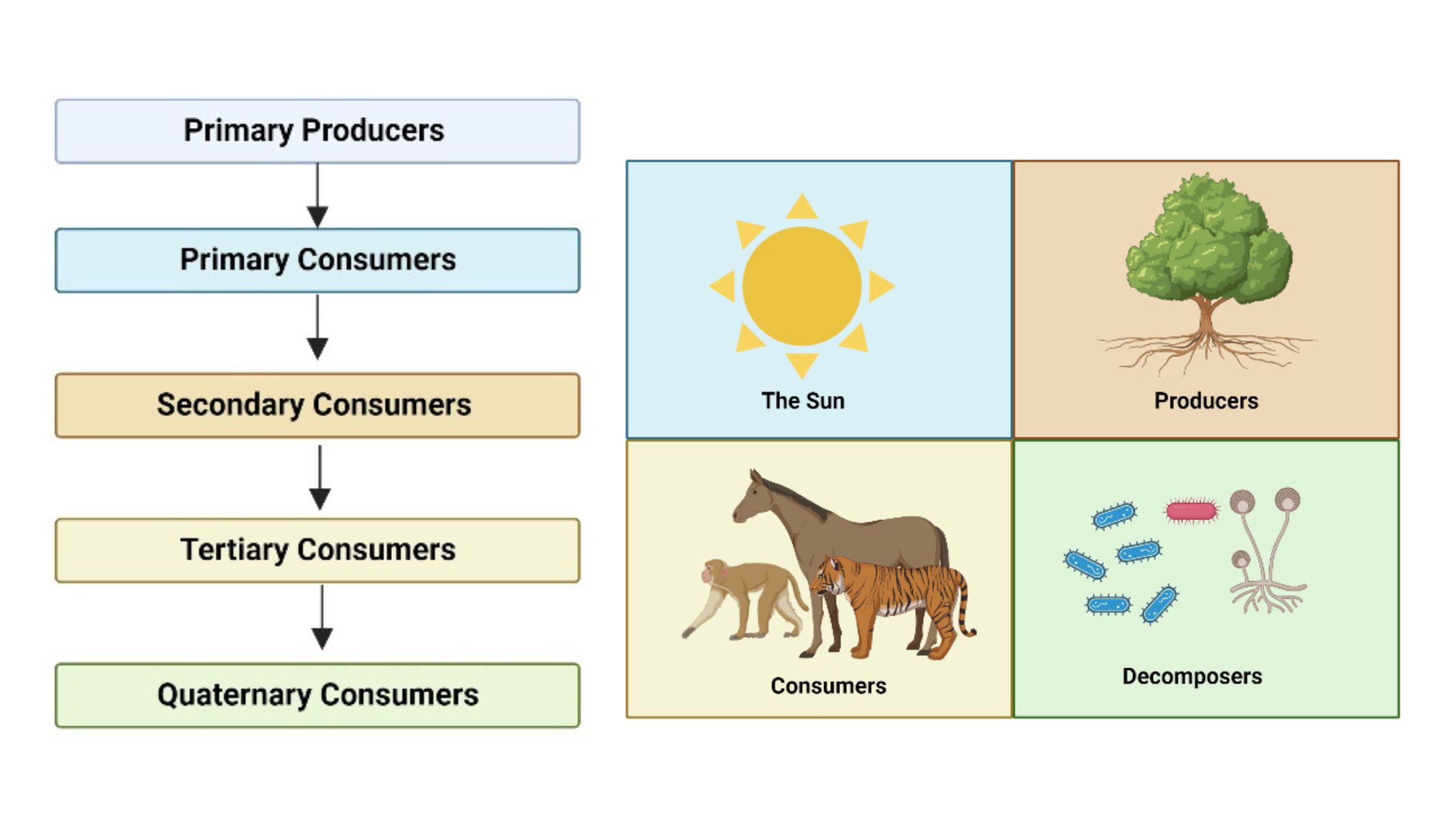
The Trophic chains or food chains are energy or nutritional cycles between the different species involved in a biological community, in which each one feeds from the previous one. Is named trophic level to each link in this chain, which determines the relationship of a species with those that are up or down in the chain: predators and food respectively. However, it is a cycle that feeds back