Explain Why All Consumers Depend On Producers For Food Biology Diagrams Uncover how primary consumers drive the food chain. Explore their vital roles, real-world examples, and the ecological impact they have on ecosystems. Understanding Primary Consumers: The Foundation of the Food Chain Primary consumers, also known as herbivores, are the crucial link between producers (plants and algae) and higher-level consumers in the intricate web of life.
Primary consumers are fundamental components of ecological food chains, holding a critical position as the link between producers and higher trophic levels.

Primary Consumer: Definition, Examples and Functions Biology Diagrams
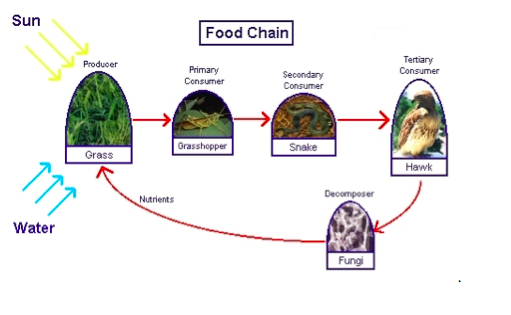
Primary Consumer Definition A primary consumer is an organism that feeds on primary producers. Organisms of this type make up the second trophic level and are consumed or predated by secondary consumers, tertiary consumers or apex predators. Trophic levels Primary consumers are usually herbivores that feed on autotrophic plants, which produce their own food through photosynthesis. Several The 4 levels of the food chain consist of: PRODUCERS: At the bottom of the food chain, plants are natural producers and provide food and nutrients to consumers. HERBIVORES: Herbivores (primary consumers) nourish plants and insects. PREDATORS: Predators (secondary consumers) prey on herbivores or other predators.

Every food chain consists of producers and consumers. In this article we look at 12 examples of primary consumers, aka herbivores.

What are 5 examples of primary consumers? Biology Diagrams
Unveiling the Four Primary Consumers in the Food Chain The term "primary consumer" refers to a crucial link in the food chain and food web. These organisms form the second trophic level, directly relying on producers (like plants and algae) for their energy. They are herbivores, meaning their diet consists solely of plant matter. Instead of pinpointing just four specific organisms as A food chain has at least three elements: a producer, a primary consumer and a secondary consumer. An example of a marine food chain is algae as producer plants, small crustaceans as primary consumers and whales as secondary consumers. In a food chain, primary consumers are assigned the task of converting plant nutrients into digestible form for secondary and tertiary consumers. Examples of primary consumers include all the plant-eating species (herbivores) found on the planet, right from leaf-cutter ants to elephants.
