Concise Medical Knowledge Biology Diagrams G 0 Phase. Not all cells undergo mitotic phase. Cells in the G 0 phase are not actively preparing to divide. The cell is in a quiescent (inactive) stage that occurs when cells exit the cell cycle. Some cells enter G 0 temporarily until an external signal triggers the onset of G 1. No more DNA replication or cell division happens at this phase. The cells that never or rarely divide include
The Enter M checkpoint influences the exit out of the G2 phase. At every transition of the cell cycle, the cells are continuously checked for DNA integrity, where (in the case of the S into G2 transition) the newly duplicated DNA is checked for mutations and fixed if necessary. Once this transition phase is passed the cell is ready for the G2

4 Major Phases of the Cell Cycle (With Diagram) Biology Diagrams
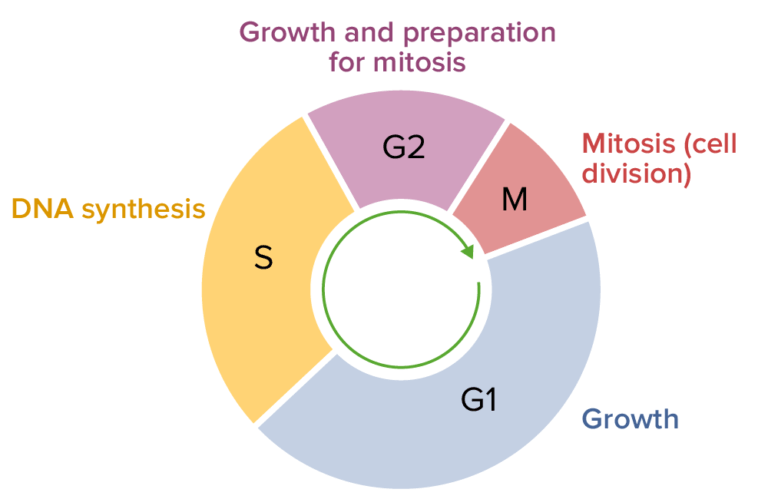
Gap 2 (G2). G1 and G2 phase represents the time of growth and preparation for mitosis. The synthesis (S) phase is the phase of cell copying or cell duplication of its DNA of its entire genome. Gap 1 (G1) This is the phase in which the cell undergoes normal growth and cell function synthesizing high amounts of proteins.
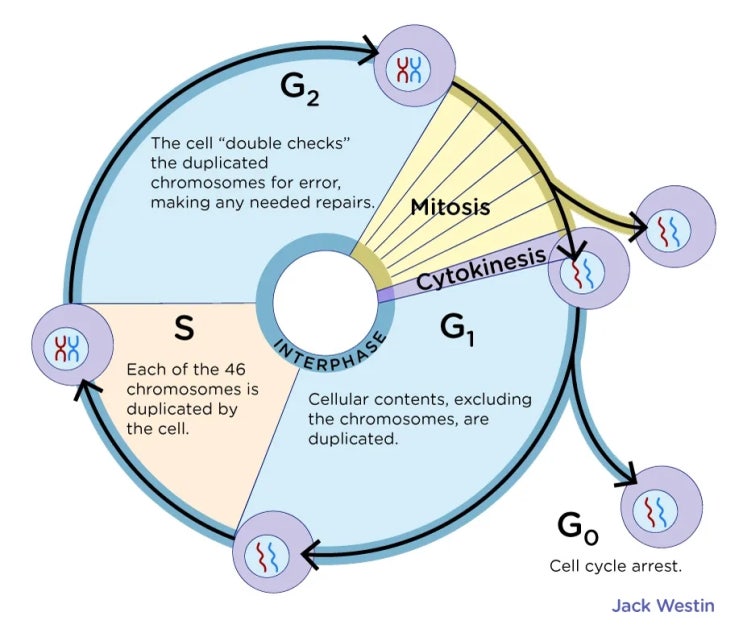
G 2 Phase. In the G 2 phase, or second gap, the cell replenishes its energy stores and synthesizes the proteins necessary for chromosome manipulation. Some cell organelles are duplicated, and the cytoskeleton is dismantled to provide resources for the mitotic spindle. There may be additional cell growth during G 2.The final preparations for the mitotic phase must be completed before the cell

G2 Phase: What Happens In This Subphase Of The Cell Cycle? Biology Diagrams
G 2 phase, Gap 2 phase, or Growth 2 phase, is the third subphase of interphase in the cell cycle directly preceding mitosis. This diagram illustrates the feedback loops underlying the G2/M transition. Cyclin-B1/CDK1 activates Plk and inactivates Wee1 and Myt1. Activated Plk activates cdc25.
